Microphones are an intrinsic part of media and communication. It uses laws of physics to increase the audibility of sound. Conversion of energy is the philosophy the working principle of the microphone is based upon. Now the question is, what is the fundamental element for this process?
Do microphones have magnets?
Yes! Microphones have magnets that convert the sound wave generated into an electrical current. The voice hitting the diaphragm vibrates and leads to the movement of the magnet near the coil.
In certain designs of the microphone, the magnet can be found to vibrate within the coil itself and thereby creating electromagnetic energy. This article is all about the use of magnets in microphones and their function.
Microphones have come a long way in transformation in terms of their mechanism. Concerning its mechanism and building nature, microphones have varied in their types.
Magnets are central to the operation of microphones and regulate the process of energy conversion. With the mediation of magnets, the sound waves are converted into electrical energy. This is further stored in the form of electrical signals. The concept of physics, the operation of microphones, is based upon the concept of electromagnetism.
Microphones having magnets
In this section, we will seek an answer to the question – Do all microphones use magnets?
Microphones using magnets as their operating mode are referred to as dynamic microphones.
In a dynamic microphone, the conversion of sound into an electrical signal takes place through the process of electromagnetism. It operates similarly to that of the diaphragm of the human vocal cord and vibrates to transmit the sound from one form of energy to the other.
While we discuss the use of magnets in microphones, we become inquisitive about whether all microphones use magnets or not.
Magnets are not used in all microphones. Magnets are mostly used in Dynamic microphones where the magnets are permanently embedded in the design of the microphone.
Magnets and microphones are intrinsically linked with one another. Magnets play a central role in the operation of the microphone.
Do microphones use magnets?
The dynamic microphones use magnets to work on the principle of electromagnetic induction. The magnets are built around the diaphragm. The microphones working with the transformer also use magnets to operate.
Electromagnetic induction is a physical phenomenon that uses magnetic energy to convert vibrations generated from sound into electrical energy.
The diaphragm placed in the dynamic microphone comes with a conductive material crucial for electromagnetic induction. The magnet creates the magnetic field, which is crucial for the operation of the microphone.
Scientifically, microphones play the role of a transducer where the conversion of sound energy into electrical energy takes place. It can be further converted into audio devices for processing as well as storing the signals.
Do all microphones use magnets?
Two types of microphones use magnets, a condenser, and a dynamic microphone.
The dynamic microphone uses the electromagnetic induction principle in order to generate signals. The material capable of being electrically conductive is cut along a magnetic flux line. It generates an electrical current of specific magnitude as well as of particular polarity. This is dependent on the speed, direction, and distance that the signal has traveled.
The ribbon mics also bring into use a metal that is flexible and micro-thin. This metal ribbon is suspended within the flux of the magnetic field. The electric-condenser mics also bring a microphone that uses plates using permanent electrostatic charge.
The condenser microphone is another type of microphone which uses the principle of electrostatic principle in the course of its operation.
Does a microphone have an electromagnet?
When we speak about the conversion of energy in a microphone, we are eager to know does a microphone have an electromagnet.
Electromagnets are there in dynamic microphones, where the microphones have the capacity to convert sound energy into electrical signals through the process of electromagnetism.
Dynamic has a lot of connotations when it is about meanings, especially in regard to music and sound. Dynamic, however, in the context of microphones, refers to the use of electromagnet or the principle of electromagnetism as a central operating mechanism.
Dynamic microphones, with the help of magnets, convert the sound waves into the signals of electric impulses. With respect to their operating mechanism, dynamic microphones have been further divided into two types, the ribbon microphones and the moving coil.
The operation of microphones and role of magnets in it.
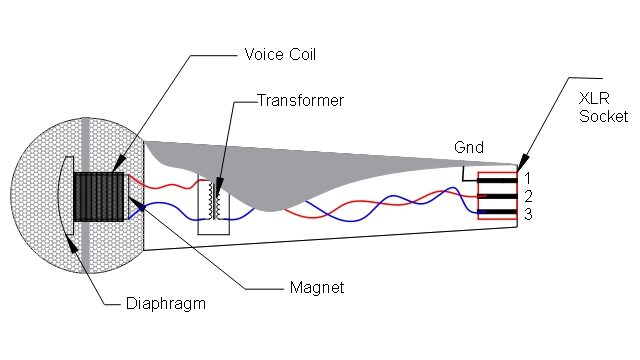
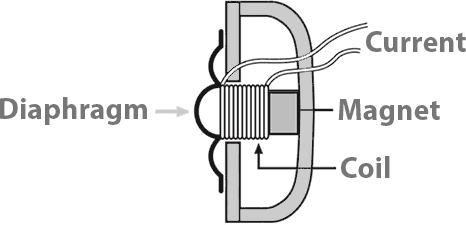
What are the microphones made of? This question will help us understand the inner structure of the microphone better. The moving coil microphones are the easiest ones in terms of operating mechanism as their built is basically that of loudspeakers. The placement of the coil is the rear part of the membrane, and surrounding the coil is a strong magnet.
When the microphone is hit by the sound wave, the coil also comes into motion. The movement that the coil undertakes is relatively within the gap of the magnet. The relative motion that the coil undertakes within the magnetic gap contributes to the creation of a small signal voltage within the coil. This device now converts sound energy into signals of electric impulse.
While it is about getting the microphones on the stage, the preference is given to the moving coil microphone as they are sturdy and do not require power from outside to operate. While it is about using microphones within the studio set up, the preference is given to the condenser.
In some cases, for microphones with a ribbon, the process is a little less robust. It also contributes to the creation of superior production of sound. However, microphones with moving coils are the most common dynamic microphone in use. The dynamic microphone is the term given to the moving coil microphones.
Working principle of the microphone.
The ways in which human diaphragms are put into use to make a sound, microphones use their diaphragm the same way to absorb the sounds. After that, it converts them into the impulse of electric current.
Now the question is, how do magnets work in microphones?
The microphone operates on the principle of electromagnetism, where the microphone transmits the sound into the current of electrical impulse, which makes the sound signal.
Other forms of the microphone (the condenser) work with the capacitance principle.
It comes with conducting plates placed parallel, which is responsible for storing the charge and thereby smoothing the signals. It brings about sound to vibrate on the plate and thereby converts the corresponding electrical signals. Then how do microphones use electromagnets?
The following section gives us the answer.
How do microphones use electromagnets – Working principle of microphone:
As far as the operating principles of microphones are concerned, they are the reverse of loudspeakers. This does not allow most people to realize how they are similar in terms of the working principle. In a loudspeaker, the flow of electricity happens in the coil of metal wire that is wrapped around a permanent magnet.
The coil is being turned into the magnetic field, where it has been pushed against the field that has been created. The coil of the microphone is attached to the diaphragm. The diaphragm is a big flat disc. The air is being pushed forth and back with this diaphragm. This continuous motion creates the wave. This is the working principle of microphone.
Ribbon Microphones
The working principle of ribbon microphones is the same as the basic principle of electromagnetic induction. This, however, does not come with a coil and membrane. It uses a narrow strip of aluminum foil, which is extremely thin. The membrane itself acts as the electric conductor, which moves with the gap of the magnet.
The aluminum ribbon, which comes in a thin piece, is much lighter than the membrane, which has the copper wire attached to it. The transducer ribbon is thereby capable of following the movement of the sound waves, which is more accurate than the movement of the coil capsule.
The presence of one conductor placed inside the magnetic gap also creates a further lower output. The ribbon microphone thereby contains a transformer that operates in the step-up model. This has the capacity of multiplying the output voltage by the factor of 30.
However, the ribbon microphone comes with lower sensitivity. The sensitivity is lower at a provided sound pressure. The ribbon mic, however, requires a preamp with low noise that comes with lots of gains.
Conclusion
In order to conclude, it can be claimed that magnets are intrinsic to the operations of microphones. It forms the central element in the conversion of sounds into electrical signals. Thank you for reading 🙂
Sources:
http://artsites.ucsc.edu/EMS/Music/tech_background/TE-20/teces_20.html




